前言
在这个专题,我们主要讨论矩阵和二叉树这两种大类的bfs做法。
BFS 有一个很经典的模板讨论,在python代码中,我们可以简单的使用queue写出他的模板公式:
def bfs():
q = collections.deque()
Step 1: q 放入第一个元素
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
Step 2: 处理cur的所有邻居
Step 3: 判断范围和符合情况
q.append(邻居)要注意,二叉树的题目中,不需要担心bfs的visited 情况,而在矩阵中,我们需要考虑visited的情况,否则会造成死循环。
接下来,我们从最简单的二叉树的bfs开始讨论。
二叉树的BFS
二叉树的BFS模板
二叉树的BFS模板,我们可以使用queue来实现,具体的代码如下:
def bfs(root):
if not root:
return
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root)
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
# do something with cur
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)接下来我们看一些例题
112. Path Sum
test cases:
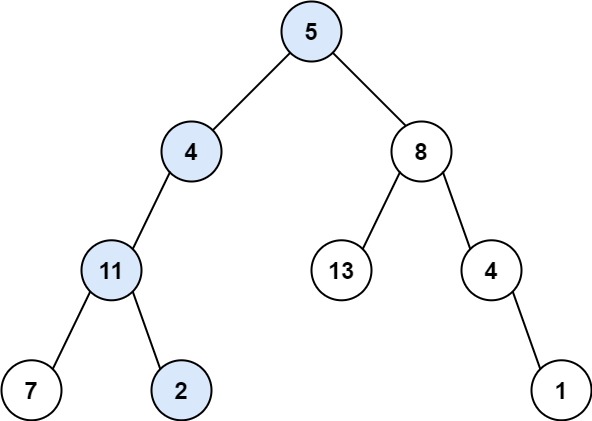
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
Output: true
Explanation: The root-to-leaf path with the target sum is shown.这道题目的意思是,给定一个二叉树,判断是否存在一条从root到leaf的路径,使得路径上的所有节点的和等于targetSum。
思路就是使用bfs来遍历所有的路径,然后判断是否有路径的和等于sum,我们来使用上面的模板来解决这道题目。
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return False
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root)
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
if not cur.left and not cur.right and cur.val == sum:
return True
if cur.left:
cur.left.val += cur.val
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
cur.right.val += cur.val
q.append(cur.right)
return False复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
test cases:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 2这道题目的意思是,给定一个二叉树,求出从root到leaf的最小深度。
思路就是使用bfs来遍历所有的路径,然后判断是否有路径的和等于sum,我们来使用上面的模板来解决这道题目。
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root)
depth = 0
while q:
depth += 1
size = len(q)
for _ in range(size):
cur = q.popleft()
if not cur.left and not cur.right:
return depth
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)
return depth复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
test cases:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 3这道题目的意思是,给定一个二叉树,求出从root到leaf的最大深度。
思路就是使用bfs来遍历所有的路径,然后判断是否有路径的和等于sum,我们来使用上面的模板来解决这道题目。
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root)
depth = 0
while q:
depth += 1
size = len(q)
for _ in range(size):
cur = q.popleft()
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)
return depth复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
test cases:
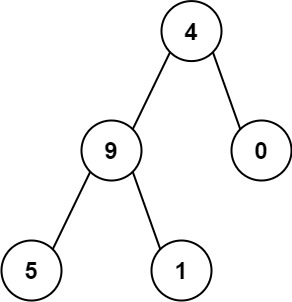
Input: root = [4,9,0,5,1]
Output: 1026
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->5 represents the number 495.
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->1 represents the number 491.
The root-to-leaf path 4->0 represents the number 40.
Therefore, sum = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026.这道题目的意思是,给定一个二叉树,求出从root到leaf的所有路径的和。
思路就是使用bfs来遍历所有的路径,然后判断是否有路径的和等于sum,我们来使用上面的模板来解决这道题目。
class Solution:
def sumNumbers(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root)
res = 0
while q:
size = len(q)
for _ in range(size):
cur = q.popleft()
if not cur.left and not cur.right:
res += cur.val
if cur.left:
cur.left.val += cur.val * 10 # 这里是关键,每次都要乘以10
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
cur.right.val += cur.val * 10 # 这里是关键,每次都要乘以10
q.append(cur.right)
return res也可以不去遍历整个queue,单独处理cur:
class Solution:
def sumNumbers(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
q = collections.deque([(root, str(root.val))])
res = []
while q:
cur, path = q.popleft()
if not cur.left and not cur.right:
res.append(path)
elif not cur.left and cur.right:
q.append((cur.right, path + str(cur.right.val)))
elif cur.left and not cur.right:
q.append((cur.left, path + str(cur.left.val)))
else:
q.append((cur.right, path + str(cur.right.val)))
q.append((cur.left, path + str(cur.left.val)))
return sum([int(path) for path in res]) # 也可以不用sum,直接在上面的if not cur.left and not cur.right:里面直接res += int(path)复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
这道题目是二叉树的bfs的模板题,我们可以直接使用上面的模板来解决这道题目。
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root) # Step 1: q 放入root元素
res = []
while q:
size = len(q) # 这里需要注意,我们需要先把当前层的size存下来,因为后面q的size会变化
level = []
for _ in range(size): # 使用for循环来遍历当前层的所有元素
cur = q.popleft() # Step 2: 处理cur的所有邻居
level.append(cur.val)
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)
res.append(level) # Step 3: 把当前层的结果放入res
return res复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
这道题跟上面的题目一样,只不过是要求从下往上遍历,我们可以直接使用上面的模板来解决这道题目。
class Solution:
def levelOrderBottom(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root) # Step 1: q 放入root元素
res = []
while q:
size = len(q) # 这里需要注意,我们需要先把当前层的size存下来,因为后面q的size会变化
level = []
for _ in range(size): # 使用for循环来遍历当前层的所有元素
cur = q.popleft() # Step 2: 处理cur的所有邻居
level.append(cur.val)
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)
res.append(level) # Step 3: 把当前层的结果放入res
return res[::-1]复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
test cases:

这道题的描述是,给定一个二叉树,返回从左到右,从右到左交替的层序遍历结果。
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[3],[20,9],[15,7]]我们可以直接使用上面的模板来解决这道题目,只不过我们需要在每一层的时候,判断当前层是奇数层还是偶数层,如果是奇数层,我们就把当前层的结果翻转一下。
class Solution:
def zigzagLevelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root) # Step 1: q 放入root元素
res = []
while q:
size = len(q) # 这里需要注意,我们需要先把当前层的size存下来,因为后面q的size会变化
level = []
for _ in range(size): # 使用for循环来遍历当前层的所有元素
cur = q.popleft() # Step 2: 处理cur的所有邻居
level.append(cur.val)
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)
if len(res) % 2 == 1: # 如果是奇数层,我们就把当前层的结果翻转一下
level = level[::-1]
res.append(level)
return res复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
199. Binary Tree Right Side View
这道题的描述是,给定一个二叉树,返回从右边看到的节点。
test cases:

Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1,3,4]我们可以直接使用上面的模板来解决这道题目,只不过我们需要在每一层的时候,把当前层的最后一个元素加入到结果中。
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return []
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root) # Step 1: q 放入root元素
res = []
while q:
size = len(q) # 这里需要注意,我们需要先把当前层的size存下来,因为后面q的size会变化
level = []
for _ in range(size): # 使用for循环来遍历当前层的所有元素
cur = q.popleft() # Step 2: 处理cur的所有邻居
level.append(cur.val)
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)
res.append(level[-1]) # 把当前层的最后一个元素加入到结果中
return res复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
这道题的描述是,给定一个完美二叉树,把每一层的节点都连接起来。
test cases:

Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above perfect binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.我们可以直接使用上面的模板来解决这道题目,只不过我们需要在每一层的时候,把当前层的最后一个元素加入到结果中。
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not root:
return root
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root) # Step 1: q 放入root元素
while q:
size = len(q) # 这里需要注意,我们需要先把当前层的size存下来,因为后面q的size会变化
for i in range(size): # 使用for循环来遍历当前层的所有元素
cur = q.popleft() # Step 2: 处理cur的所有邻居
if i < size - 1: # 如果不是当前层的最后一个元素,那么就把cur的next指向q[0]
cur.next = q[0]
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)
return root复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
这道题的描述是,给定一个二叉树,把每一层的节点都连接起来。
test cases:
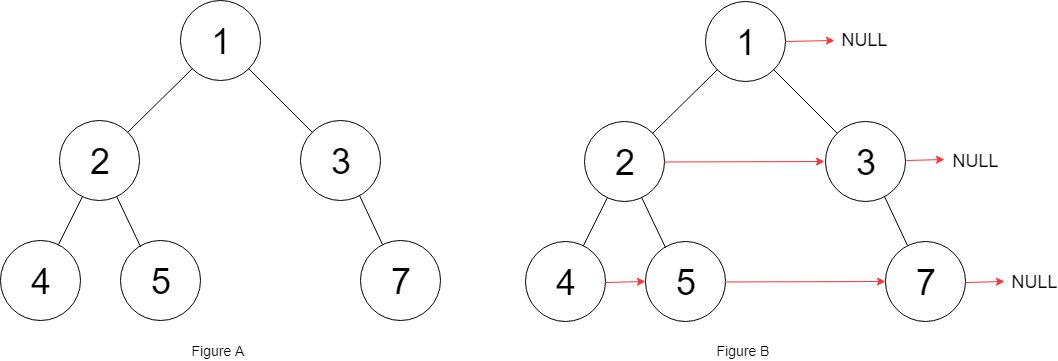
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.我们可以直接使用上面的模板来解决这道题目,只不过我们需要在每一层的时候,把当前层的最后一个元素加入到结果中。
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not root:
return root
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root) # Step 1: q 放入root元素
while q:
size = len(q) # 这里需要注意,我们需要先把当前层的size存下来,因为后面q的size会变化
for i in range(size): # 使用for循环来遍历当前层的所有元素
cur = q.popleft() # Step 2: 处理cur的所有邻居
if i < size - 1: # 如果不是当前层的最后一个元素,那么就把cur的next指向q[0]
cur.next = q[0]
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)
return root复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
矩阵的BFS
200. Number of Islands
这道题的描述是,给定一个二维数组,其中 1 表示陆地,0 表示水,求岛屿的数量。求岛屿的数量,就是求连通分量的数量。
test cases:
Input: grid = [
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
Output: 3我们可以使用 BFS 来解决这道题目,我们可以把每一个陆地都当做是一个起始点,然后使用 BFS 来遍历这个岛屿,把这个岛屿的所有陆地都标记成已经访问过,然后继续遍历下一个岛屿。注意这里是矩阵,是有可能造成死循环,所以我们需要使用一个 visited 数组来记录是否访问过。
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return grid
row = len(grid)
col = len(grid[0])
count = 0
visited = [[0 for _ in range(col)] for _ in range(row)] # 用来标记是否访问过
def bfs(grid, i, j):
q = collections.deque([(i, j)])
visited[i][j] = 1
while q:
cur_x, cur_y = q.popleft()
for x, y in (cur_x + 1, cur_y), (cur_x - 1, cur_y), (cur_x, cur_y + 1), (cur_x, cur_y - 1): # 上下左右四个方向
if 0 <= x < row and 0 <= y < col and not visited[x][y] and grid[x][y] == "1": # 如果是陆地,那么就把它放入队列中
q.append((x, y))
visited[x][y] = 1
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if not visited[i][j] and grid[i][j] == "1":
bfs(grid, i, j)
count += 1
return count当然这道题完全可以不去使用 visited 数组,我们可以直接把 grid[i][j] = "#" 来标记已经访问过的陆地。
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return grid
row = len(grid)
col = len(grid[0])
count = 0
def bfs(grid, i, j):
q = collections.deque([(i, j)])
grid[i][j] = "#" # 标记已经访问过的陆地
while q:
cur_x, cur_y = q.popleft()
for x, y in (cur_x + 1, cur_y), (cur_x - 1, cur_y), (cur_x, cur_y + 1), (cur_x, cur_y - 1): # 上下左右四个方向
if 0 <= x < row and 0 <= y < col and grid[x][y] == "1": # 如果是陆地,那么就把它放入队列中
q.append((x, y))
grid[x][y] = "#"
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if grid[i][j] == "1":
bfs(grid, i, j)
count += 1
return count复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。因为我们最多遍历一次矩阵中的全部元素。
- 空间复杂度:O(min(M,N)),在最坏的情况下(全部为陆地),队列的大小可以达到 min(M,N)。
542. 01 Matrix
这道题的描述是,给定一个二维数组,其中 0 表示海洋,1 表示陆地,求每一个陆地距离最近的海洋的距离。
test cases:
Input:
[[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[1,1,1]]
Output:
[[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[1,2,1]]这道题的思路是,我们可以把所有的海洋都当做是起始点,然后使用 BFS 来遍历陆地,把陆地的距离都标记成已经访问过,然后继续遍历下一个海洋。注意这里是矩阵,是有可能造成死循环,所以我们需要使用一个 visited 数组来记录是否访问过。
class Solution:
def updateMatrix(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
q = deque()
visited = set()
for i in range(len(mat)):
for j in range(len(mat[0])):
if mat[i][j] == 0:
q.append((i, j)) # 把所有的海洋都当做是起始点
visited.add((i, j))
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
for x, y in (i + 1, j), (i - 1, j), (i, j + 1), (i, j - 1):
if 0 <= x < len(mat) and 0 <= y < len(mat[0]) and (x, y) not in visited:
mat[x][y] = mat[i][j] + 1
visited.add((x, y))
q.append((x, y))
return mat复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。因为我们最多遍历一次矩阵中的全部元素。
- 空间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。主要为队列的开销。
994. Rotting Oranges
这道题的描述是,给定一个二维数组,其中 0 表示空,1 表示新鲜橘子,2 表示腐烂的橘子,求腐烂所有橘子所需要的最少的时间。如果不能腐烂所有橘子,那么返回 -1。
test cases:
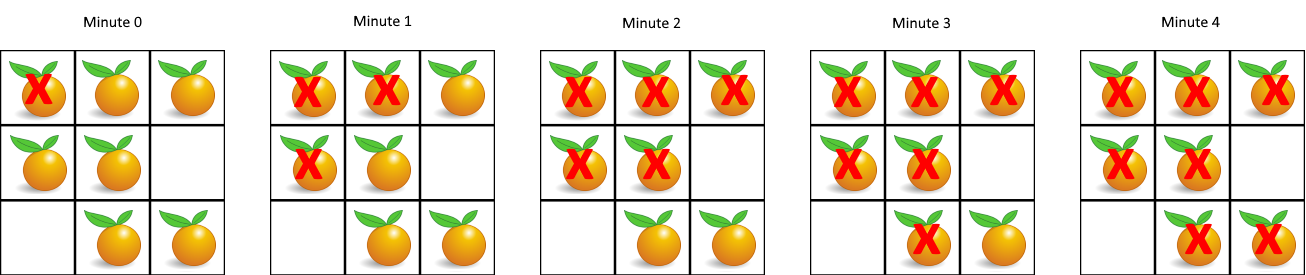
Input: [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
Output: 4这道题的思路是,我们可以把所有的腐烂的橘子都当做是起始点,然后使用 BFS 来遍历新鲜橘子,把新鲜橘子的状态都标记成已经访问过,然后继续遍历下一个腐烂的橘子。注意这里是矩阵,是有可能造成死循环,所以我们需要使用一个 visited 数组来记录是否访问过。
class Solution:
def orangesRotting(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
q = deque()
visited = set()
fresh = 0
time = 0
for i in range(len(grid)):
for j in range(len(grid[0])):
if grid[i][j] == 2:
q.append((i, j)) # 把所有的腐烂的橘子都当做是起始点
visited.add((i, j))
elif grid[i][j] == 1:
fresh += 1
if fresh == 0:
return 0
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
i, j = q.popleft()
for x, y in (i + 1, j), (i - 1, j), (i, j + 1), (i, j - 1):
if 0 <= x < len(grid) and 0 <= y < len(grid[0]) and (x, y) not in visited and grid[x][y] == 1:
fresh -= 1
visited.add((x, y))
q.append((x, y))
time += 1
return time - 1 if fresh == 0 else -1复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。因为我们最多遍历一次矩阵中的全部元素。
- 空间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。主要为队列的开销。
1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix
这道题的描述是,给定一个二维数组,其中 0 表示空,1 表示障碍物,求从左上角到右下角的最短路径的长度。如果不能到达,那么返回 -1。
test cases:
Input: [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
Output: 4这道题的思路是,我们可以把所有的空都当做是起始点,然后使用 BFS 来遍历障碍物,把障碍物的状态都标记成已经访问过,然后继续遍历下一个空。注意这里是矩阵,是有可能造成死循环,所以我们需要使用一个 visited 数组来记录是否访问过。
class Solution:
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
q = deque()
visited = set()
n = len(grid)
if grid[0][0] == 1 or grid[n - 1][n - 1] == 1:
return -1
q.append((0, 0))
visited.add((0, 0))
time = 0
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
i, j = q.popleft()
if i == n - 1 and j == n - 1:
return time + 1
for x, y in (i + 1, j), (i - 1, j), (i, j + 1), (i, j - 1), (i + 1, j + 1), (i - 1, j - 1), (i + 1, j - 1), (i - 1, j + 1):
if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < n and (x, y) not in visited and grid[x][y] == 0:
visited.add((x, y))
q.append((x, y))
time += 1
return -1复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。因为我们最多遍历一次矩阵中的全部元素。
- 空间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。主要为队列的开销。
1162. As Far from Land as Possible
这道题的描述是,给定一个二维数组,其中 0 表示海洋,1 表示陆地,求海洋中离陆地最远的距离。如果没有海洋或者陆地,那么返回 -1。
test cases:
Input: [[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]
Output: 2这道题的思路是,我们可以把所有的陆地都当做是起始点,然后使用 BFS 来遍历海洋,把海洋的状态都标记成已经访问过,然后继续遍历下一个陆地。注意这里是矩阵,是有可能造成死循环,所以我们需要使用一个 visited 数组来记录是否访问过。
class Solution:
def maxDistance(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
q = deque()
visited = set()
n = len(grid)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == 1:
q.append((i, j))
visited.add((i, j))
if len(q) == 0 or len(q) == n * n:
return -1
time = 0
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
i, j = q.popleft()
for x, y in (i + 1, j), (i - 1, j), (i, j + 1), (i, j - 1):
if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < n and (x, y) not in visited and grid[x][y] == 0:
visited.add((x, y))
q.append((x, y))
time += 1
return time - 1复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。因为我们最多遍历一次矩阵中的全部元素。
- 空间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。主要为队列的开销。
733. Flood Fill
这道题的描述是给定一个矩阵,去填充一个新的颜色,然后这个颜色会从一个点开始向四周扩散,直到遇到和原来颜色不一样的颜色为止。
test cases:
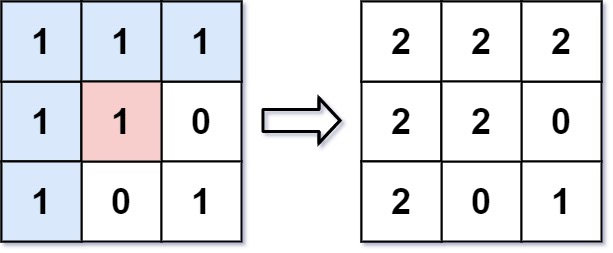
Input: image = [[1,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,1]], sr = 1, sc = 1, color = 2
Output: [[2,2,2],[2,2,0],[2,0,1]]
Explanation: From the center of the image with position (sr, sc) = (1, 1) (i.e., the red pixel), all pixels connected by a path of the same color as the starting pixel (i.e., the blue pixels) are colored with the new color.
Note the bottom corner is not colored 2, because it is not 4-directionally connected to the starting pixel.这道题的思路就是,我们可以使用 DFS 或者 BFS 来遍历所有和起始点颜色一样的点,然后把这些点都标记成新的颜色。
class Solution:
def floodFill(self, image: List[List[int]], sr: int, sc: int, color: int) -> List[List[int]]:
q = collections.deque([(sr, sc)])
old_color = image[sr][sc]
visited = set()
visited.add((sr, sc))
image[sr][sc] = color
while q:
x, y = q.popleft()
for i, j in (x + 1, y), (x - 1, y), (x, y + 1), (x, y - 1):
if 0 <= i < len(image) and 0 <= j < len(image[0]) and image[i][j] == old_color and (i, j) not in visited:
image[i][j] = color
q.append((i, j))
visited.add((i, j))
return image复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。因为我们最多遍历一次矩阵中的全部元素。
- 空间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。主要为队列的开销。
490. The Maze
这道题的描述是,给定一个二维数组,其中 0 表示空地,1 表示墙,球可以从空地滚动,直到碰到墙为止。求球是否可以滚动到终点。
test cases:
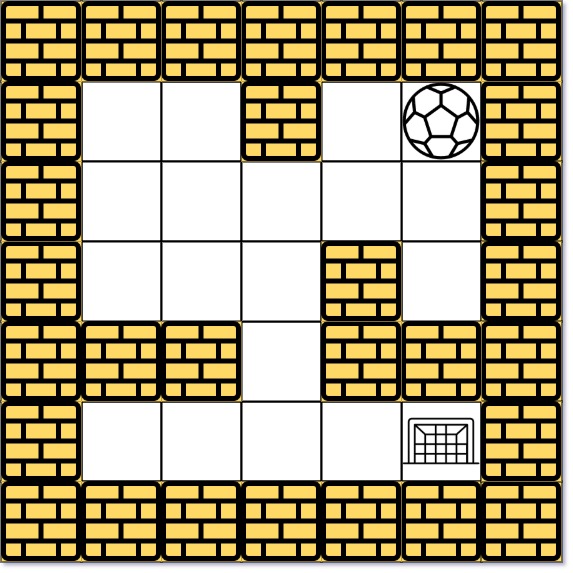
Input: maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [4,4]
Output: true
Explanation: One possible way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right.这道题的思路是,我们可以使用 BFS 来遍历所有的点,然后把所有的点都标记成已经访问过,如果遇到墙,那么就停止,如果遇到终点,那么就返回 True。
class Solution:
import collections
def hasPath(self, maze: List[List[int]], start: List[int], destination: List[int]) -> bool:
rows = len(maze)
cols = len(maze[0])
dir = [1, 0, -1, 0, 1]
visited = [[0 for _ in range(cols)] for _ in range(rows)]
q = deque()
q.append(start)
visited[start[0]][start[1]] = 1
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
if cur[0] == destination[0] and cur[1] == destination[1]:
return True
for i in range(4):
newX = cur[0]
newY = cur[1]
while 0 <= newX < rows and 0 <= newY < cols and maze[newX][newY] != 1:
newX += dir[i]
newY += dir[i + 1]
newX -= dir[i]
newY -= dir[i + 1]
if visited[newX][newY]: continue
q.append([newX, newY])
visited[newX][newY] = 1
return False复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。因为我们最多遍历一次矩阵中的全部元素。
- 空间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。主要为队列的开销。
505. The Maze II
这道题的描述是,给定一个二维数组,其中 0 表示空地,1 表示墙,球可以从空地滚动,直到碰到墙为止。求球从起点到终点的最短距离。
test cases:

Input: maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [4,4]
Output: 12
Explanation: One possible way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right.
The length of the path is 1 + 1 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12.这道题的思路是,我们可以使用 BFS 来遍历所有的点,但是与前一个题不一样的点是他需要计算距离,所以我们需要使用一个二维数组来记录每个点到起点的距离,然后在遍历的时候,如果发现当前点到起点的距离比之前记录的距离小,那么就更新距离。
class Solution:
import collections
import sys
def shortestDistance(self, maze: List[List[int]], start: List[int], destination: List[int]) -> int:
rows = len(maze)
cols = len(maze[0])
dir = [1, 0, -1, 0, 1]
res = [[float('inf') for _ in range(cols)] for _ in range(rows)]
q = deque()
q.append([start[0], start[1], 0])
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
if cur[2] >= res[cur[0]][cur[1]]:
continue
res[cur[0]][cur[1]] = cur[2]
for i in range(4):
newX = cur[0]
newY = cur[1]
path = cur[2]
while 0 <= newX < rows and 0 <= newY < cols and maze[newX][newY] == 0:
newX += dir[i]
newY += dir[i + 1]
path += 1
newX -= dir[i]
newY -= dir[i + 1]
path -= 1
q.append([newX, newY, path])
return -1 if res[destination[0]][destination[1]] == float('inf') 







Comments NOTHING