前言
这个专题主要是关于图的算法,图的算法题其实主要就是通过构建图的数据结构,然后对图进行遍历,从而解决问题。
遍历的方法有两种,一种是深度优先遍历,一种是广度优先遍历。
总的来说,这种类型的题,时间复杂度往往都是 O(N),因为每个节点都只需要遍历一遍。
让我们来看一些例题,这里面包含一些我们专题总结过的题,不过这里我们会同时通过 BFS 和 DFS 来解决,好让我们知道两种方法的区别。
matrix
200. number of islands
这个题目是一个非常经典的题目,我们可以通过 DFS 和 BFS 来解决。
test cases:
input:
[
["1","1","1","1","0"],
["1","1","0","1","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","0","0","0"]
]
output: 1
input:
[
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
output: 3DFS:
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
def dfs(grid, i, j):
grid[i][j] = '0'
for x, y in (i + 1, j), (i - 1, j), (i, j + 1), (i, j - 1):
if 0 <= x < len(grid) and 0 <= y < len(grid[0]) and grid[x][y] == '1':
dfs(grid, x, y)
count = 0
for i in range(len(grid)):
for j in range(len(grid[i])):
if grid[i][j] == '1':
dfs(grid, i, j)
count += 1
return countBFS:
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return grid
row = len(grid)
col = len(grid[0])
count = 0
def bfs(grid, i, j):
q = collections.deque([(i, j)])
grid[i][j] = "#" # 标记已经访问过的陆地
while q:
cur_x, cur_y = q.popleft()
for x, y in (cur_x + 1, cur_y), (cur_x - 1, cur_y), (cur_x, cur_y + 1), (cur_x, cur_y - 1): # 上下左右四个方向
if 0 <= x < row and 0 <= y < col and grid[x][y] == "1": # 如果是陆地,那么就把它放入队列中
q.append((x, y))
grid[x][y] = "#"
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if grid[i][j] == "1":
bfs(grid, i, j)
count += 1
return count复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。
- 空间复杂度:O(MN),在最坏情况下,整个网格均为陆地,深度优先搜索的深度达到 MN。
130. surrounded regions
这个题目的描述就是,给定一个二维的矩阵,里面有 X 和 O,我们需要把被 X 包围的 O 变成 X。
test cases:
input:
[
["X","X","X","X"],
["X","O","O","X"],
["X","X","O","X"],
["X","O","X","X"]
]
output:
[
["X","X","X","X"],
["X","X","X","X"],
["X","X","X","X"],
["X","O","X","X"]
]这道题的思路是,我们先把边界上的 O 变成 E,然后再把里面的 O 变成 X,最后再把 E 变成 O。
BFS:
class Solution:
def solve(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
if not board:
return board
from itertools import product
borders = list(
product(
range(len(board)),
[0, len(board[0]) - 1]
)) \
+ list(
product(
[0, len(board) - 1],
range(len(board[0]))
))
def bfs(board, i, j):
q = collections.deque([(i, j)])
while q:
cur_x, cur_y = q.popleft()
if board[cur_x][cur_y] != "O":
continue
board[cur_x][cur_y] = "E"
for x, y in (cur_x + 1, cur_y), (cur_x - 1, cur_y), (cur_x, cur_y + 1), (cur_x, cur_y - 1):
if 0 <= x < len(board) and 0 <= y < len(board[0]):
q.append((x, y))
for i, j in borders:
if board[i][j] != "O":
continue
bfs(board, i, j)
for line in board:
print(line)
for r in range(len(board)):
for c in range(len(board[0])):
if board[r][c] == 'O': board[r][c] = 'X' # captured
elif board[r][c] == 'E': board[r][c] = 'O' # escapedDFS:
class Solution:
def solve(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
if not board:
return board
from itertools import product
borders = list(
product(
range(len(board)),
[0, len(board[0]) - 1]
)) \
+ list(
product(
[0, len(board) - 1],
range(len(board[0]))
))
def dfs(board, i, j):
if board[i][j] != "O":
return
board[i][j] = "E"
for x, y in (i + 1, j), (i - 1, j), (i, j + 1), (i, j - 1):
if 0 <= x < len(board) and 0 <= y < len(board[0]):
dfs(board, x, y)
for i, j in borders:
if board[i][j] != "O":
continue
dfs(board, i, j)
for r in range(len(board)):
for c in range(len(board[0])):
if board[r][c] == 'O': board[r][c] = 'X' # captured
elif board[r][c] == 'E': board[r][c] = 'O' # escaped复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。
- 空间复杂度:O(MN),在最坏情况下,整个网格均为陆地,深度优先搜索的深度达到 MN。
417. pacific atlantic water flow
这个题目的描述就是,给定一个二维的矩阵,给出能同时流向太平洋和大西洋的坐标。
test cases:
Input: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
Output: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
Explanation: The following cells can flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, as shown below:
[0,4]: [0,4] -> Pacific Ocean
[0,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[1,3]: [1,3] -> [0,3] -> Pacific Ocean
[1,3] -> [1,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[1,4]: [1,4] -> [1,3] -> [0,3] -> Pacific Ocean
[1,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[2,2]: [2,2] -> [1,2] -> [0,2] -> Pacific Ocean
[2,2] -> [2,3] -> [2,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[3,0]: [3,0] -> Pacific Ocean
[3,0] -> [4,0] -> Atlantic Ocean
[3,1]: [3,1] -> [3,0] -> Pacific Ocean
[3,1] -> [4,1] -> Atlantic Ocean
[4,0]: [4,0] -> Pacific Ocean
[4,0] -> Atlantic Ocean
Note that there are other possible paths for these cells to flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.这道题的思路是,从边界开始,分别找到能流向太平洋和大西洋的坐标,然后求交集。
BFS:
class Solution:
def bfs(self, ocean, heights):
q = collections.deque(ocean)
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
for x, y in (i + 1, j), (i - 1, j), (i, j + 1), (i, j - 1):
if 0 <= x < len(heights) and 0 <= y < len(heights[0]) and (x, y) not in ocean and heights[x][y] >= heights[i][j]:
q.append((x, y))
ocean.add((x, y))
return ocean
def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
if not heights: return []
w, h = len(heights[0]), len(heights)
pacific = set([(i, 0) for i in range(h)] + [(0, j) for j in range(w)])
atlantic = set([(i, w - 1) for i in range(h)] + [(h - 1, j) for j in range(w)])
return list(self.bfs(pacific, heights) & self.bfs(atlantic, heights))323. number of connected components in an undirected graph
这个题目的描述就是,给定一个无向图,求出有多少个连通的部分。
test cases:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: 2这道题的思路是,使用 DFS 或者 BFS 遍历图,然后记录遍历过的节点,最后返回遍历过的次数。
BFS:
class Solution:
def countComponents(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
graph[edge[1]].append(edge[0])
visited = set()
def bfs(i):
q = collections.deque([i])
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
for nxt in graph[cur]:
if nxt not in visited:
visited.add(nxt)
q.append(nxt)
res = 0
for i in range(n):
if i not in visited:
bfs(i)
res += 1
return resDFS:
class Solution:
def countComponents(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
graph[edge[1]].append(edge[0])
visited = set()
def dfs(i):
for nxt in graph[i]:
if nxt not in visited:
visited.add(nxt)
dfs(nxt)
res = 0
for i in range(n):
if i not in visited:
dfs(i)
res += 1
return res复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(n + e)$
- 空间复杂度:$O(n + e)$
261. graph valid tree
这个题目的描述就是,给定一个无向图,判断是否是一棵树。
test cases:
Input: n = 5, and edges = [[0,1], [0,2], [0,3], [1,4]]
Output: true这道题的思路是,使用 DFS 或者 BFS 遍历图,然后判断是否有环。
BFS:
class Solution(object):
def validTree(self, n, edges):
"""
:type n: int
:type edges: List[List[int]]
:rtype: bool
"""
if len(edges) != n - 1:
return False
graph = [set() for _ in range(n)]
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].add(edge[1])
graph[edge[1]].add(edge[0])
visited = set()
parent = {}
q = collections.deque([0])
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
visited.add(cur)
for nxt in graph[cur]:
if nxt not in visited:
parent[nxt] = cur # 这里记录的是父节点
q.append(nxt)
elif nxt != parent[cur]: # 如果当前节点已经访问过了,但是不是父节点,说明有环
print(parent)
return False
print(parent)
return len(visited) == n同时这题可以尝试用 Topological Sort 来做,但是这里需要注意的是,我们需要判断是否有环,如果有环的话,就不是一棵树了。
class Solution(object):
def validTree(self, n, edges):
"""
:type n: int
:type edges: List[List[int]]
:rtype: bool
"""
if len(edges) != n - 1:
return False
graph = [set() for _ in range(n)]
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].add(edge[1])
graph[edge[1]].add(edge[0])
indegrees = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
indegrees[i] = len(graph[i])
queue = deque([i for i, degrees in enumerate(indegrees) if degrees == 1])
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
for child in graph[node]:
indegrees[child] -= 1
if indegrees[child] == 1:
queue.append(child)
return all(degree == 0 for degree in indegrees)1926. nearest exit from entrance in maze
这个题目的描述就是,给定一个二维的矩阵,里面有 . 和 +,我们需要找到从入口到出口的最短路径。
test cases:
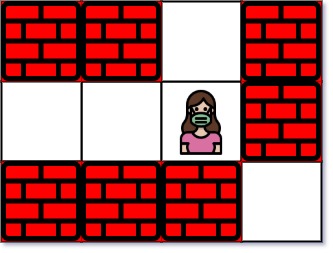
Input: maze = [["+","+",".","+"],[".",".",".","+"],["+","+","+","."]], entrance = [1,2]
Output: 1
Explanation: There are 3 exits in this maze at [1,0], [0,2], and [2,3].
Initially, you are at the entrance cell [1,2].
- You can reach [1,0] by moving 2 steps left.
- You can reach [0,2] by moving 1 step up.
It is impossible to reach [2,3] from the entrance.
Thus, the nearest exit is [0,2], which is 1 step away.这道题的思路是,我们需要先找到所有的出口,然后再从入口开始做 BFS,直到找到出口。
class Solution:
def nearestExit(self, maze: List[List[str]], entrance: List[int]) -> int:
q = collections.deque([(entrance[0], entrance[1], 0)])
visited = set()
visited.add(tuple(entrance))
min_step = float("inf")
def is_border(i, j):
if entrance != [i, j]:
return i in [0, len(maze) - 1] or j in [0, len(maze[0]) - 1]
return False
while q:
i, j, step = q.popleft()
if is_border(i, j):
min_step = min(min_step, step)
break
for x, y in (i + 1, j), (i - 1, j), (i, j - 1), (i, j + 1):
if 0 <= x < len(maze) and 0 <= y < len(maze[0]) and (x, y) not in visited and maze[x][y] == ".":
q.append((x, y, step + 1))
visited.add((x, y))
return min_step if min_step != float("inf") else -1复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(MN),其中 M 和 N 分别为行数和列数。
- 空间复杂度:O(MN),在最坏情况下,整个网格均为陆地,深度优先搜索的深度达到 MN。
133. clone graph
这个题目的描述就是,给定一个无向图,我们需要克隆这个图。
test cases:
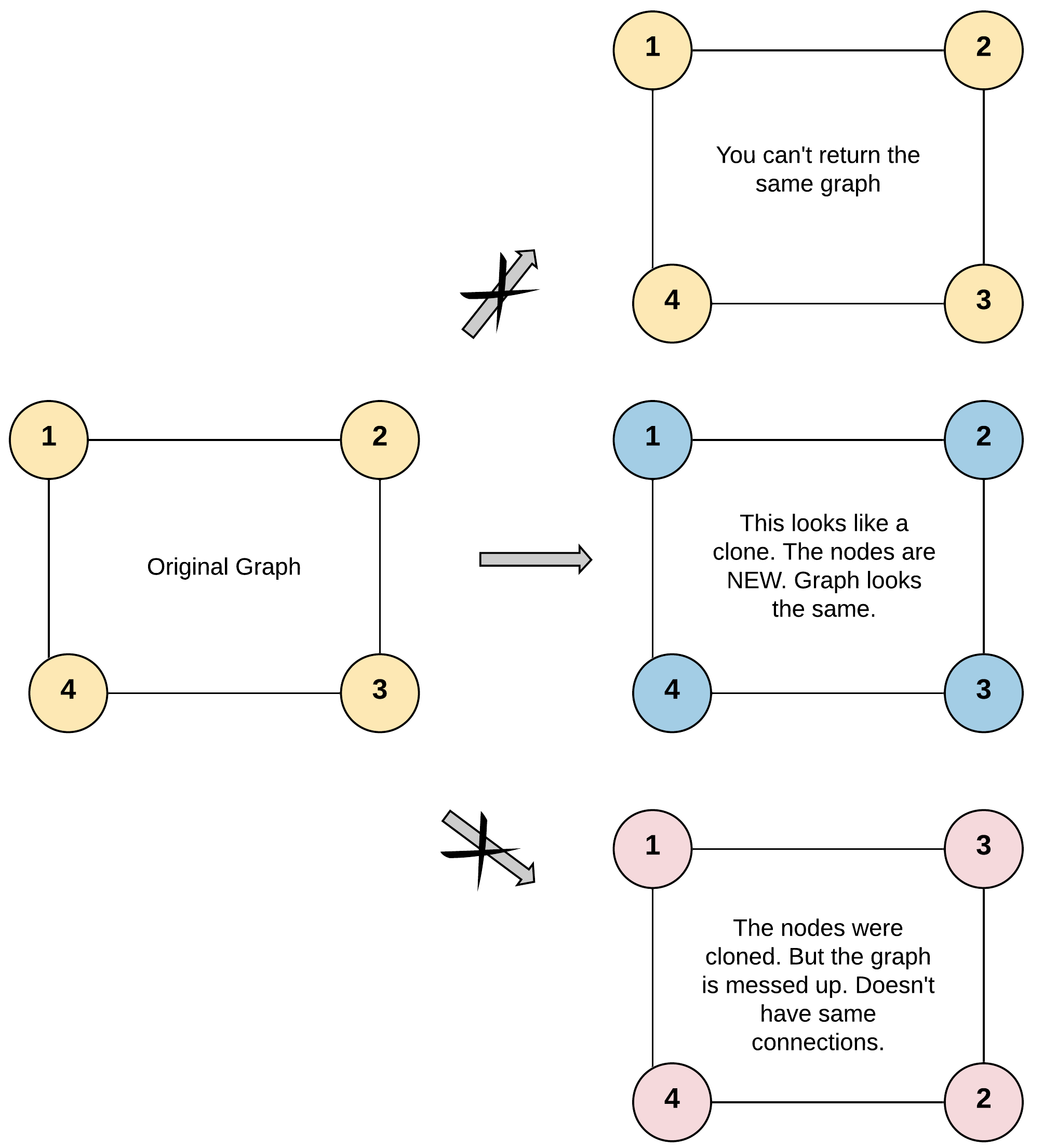
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph.
1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).这道题的思路是,我们需要用一个字典来记录已经访问过的节点,然后用 BFS 或者 DFS 来遍历整个图。
BFS:
class Solution:
def cloneGraph(self, node: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not node:
return node
visited = {}
q = collections.deque([node])
visited[node] = Node(node.val, [])
while q:
cur_node = q.popleft()
for neighbor in cur_node.neighbors:
if neighbor not in visited:
visited[neighbor] = Node(neighbor.val, [])
q.append(neighbor)
visited[cur_node].neighbors.append(visited[neighbor])
return visited[node]DFS:
class Solution:
def cloneGraph(self, node: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not node:
return node
visited = {}
def dfs(node):
if node in visited:
return visited[node]
visited[node] = Node(node.val, [])
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
visited[node].neighbors.append(dfs(neighbor))
return visited[node]
return dfs(node)复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是图中节点的数量。深度优先搜索遍历图的过程中每个节点只会被访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是图中节点的数量。空间复杂度主要取决于存储所有节点的开销,即为 O(N)。
构建
399. evaluate division
这个题目的描述是,给定一些除法式子,比如 a / b = 2.0, b / c = 3.0.,然后给定一些查询,比如 a / c, b / a, a / e, a / a, x / x.,我们需要根据已知的除法式子来计算这些查询的结果。
test cases:
Input:
equations = [ ["a", "b"], ["b", "c"] ],
values = [2.0, 3.0],
queries = [ ["a", "c"], ["b", "a"], ["a", "e"], ["a", "a"], ["x", "x"] ].
Output: [6.0, 0.5, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0 ]这道题的思路是,我们需要用一个字典来记录已经访问过的节点,然后用 BFS 或者 DFS 来遍历整个图。
BFS:
class Solution:
def calcEquation(self, equations: List[List[str]], values: List[float], queries: List[List[str]]) -> List[float]:
graph = collections.defaultdict(dict)
for equation, value in zip(equations, values):
src = equation[0]
dst = equation[1]
graph[src][dst] = value
graph[dst][src] = 1 / value
def bfs(graph, src, dst):
if not graph:
return -1
if src not in graph:
return -1
q = collections.deque([(src, 1)])
visited = set()
visited.add(src)
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
if cur[0] == dst:
return cur[1]
for nxt in graph[cur[0]]:
if nxt not in visited:
q.append((nxt, cur[1] * graph[cur[0]][nxt]))
visited.add(nxt)
return -1
res = []
for query in queries:
res.append(bfs(graph, query[0], query[1]))
return res复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N + M),其中 N 是方程式的数量,M 是方程式中字符数量的总和。对于每个查询,我们需要 O(M) 的时间来找到对应的边。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是方程式的数量。我们需要 O(N) 的空间来存储图。
841. keys and rooms
这个题目的描述是,给定一个二维数组,每个数组里面的元素是一个数组,表示房间里面的钥匙,我们需要判断是否能够进入所有的房间。
test cases:
Input: [[1],[2],[3],[]]
Output: true
Input: [[1,3],[3,0,1],[2],[0]]
Output: false这道题的思路是,我们需要先构建一个 graph,存储每个房间里面的钥匙,然后用 BFS 或者 DFS 来遍历整个图。
BFS:
class Solution:
def canVisitAllRooms(self, rooms: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = collections.defaultdict(set)
for i in range(len(rooms)):
for key in rooms[i]:
graph[i].add(key)
q = collections.deque([0])
visited = set()
visited.add(0)
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
for nxt in graph[cur]:
if nxt not in visited:
q.append(nxt)
visited.add(nxt)
return len(visited) == len(rooms)DFS:
class Solution:
def canVisitAllRooms(self, rooms: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = collections.defaultdict(set)
for i in range(len(rooms)):
for key in rooms[i]:
graph[i].add(key)
def dfs(graph, cur, visited):
if cur in visited:
return
visited.add(cur)
for nxt in graph[cur]:
dfs(graph, nxt, visited)
visited = set()
dfs(graph, 0, visited)
return len(visited) == len(rooms)DFS 2 (用 stack):
class Solution:
def canVisitAllRooms(self, rooms: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = collections.defaultdict(set)
for i in range(len(rooms)):
for key in rooms[i]:
graph[i].add(key)
stack = [0]
visited = set()
while stack:
cur = stack.pop()
if cur in visited:
continue
visited.add(cur)
for nxt in graph[cur]:
stack.append(nxt)
return len(visited) == len(rooms)复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N + M),其中 N 是房间的数量,M 是所有房间里面钥匙的数量。我们需要 O(M) 的时间来构建图。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是房间的数量。我们需要 O(N) 的空间来存储图。
547. Number of Provinces
这个题目的描述是,给出一个 isConnected 的二维数组,我们需要判断有多少个省份。
test cases:
Input: isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]]
Output: 2
Input: isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
Output: 3这道题的思路是,我们需要先构建一个 graph,然后通过以所有的节点为起点,用 BFS 或者 DFS 来遍历整个图。
BFS:
class Solution:
def findCircleNum(self, isConnected: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = collections.defaultdict(set)
for i in range(len(isConnected)):
for j in range(len(isConnected[0])):
if i != j and isConnected[i][j] == 1:
graph[i].add(j)
q = collections.deque(graph.keys())
visited = set()
count = 0
for i in range(len(isConnected)):
if i not in visited:
q = collections.deque([i])
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
for nxt in graph[cur]:
if nxt not in visited:
visited.add(nxt)
q.append(nxt)
count += 1
return countDFS:
class Solution:
def findCircleNum(self, isConnected: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = collections.defaultdict(set)
for i in range(len(isConnected)):
for j in range(len(isConnected[0])):
if i != j and isConnected[i][j] == 1:
graph[i].add(j)
def dfs(graph, cur, visited):
if cur in visited:
return
visited.add(cur)
for nxt in graph[cur]:
dfs(graph, nxt, visited)
visited = set()
count = 0
for i in range(len(isConnected)):
if i not in visited:
dfs(graph, i, visited)
count += 1
return count909. snakes and ladders
这个题目的描述是,给出一个 N x N 的棋盘,每个格子里面有一个数字,如果当前的格子里面的数字不是 -1,那么我们可以跳到这个数字所在的格子里面,如果当前的格子里面的数字是 -1,那么我们就不能跳到这个格子里面。我们需要判断从左上角到右下角的最小步数。
test cases:
Input: board = [[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1],
[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1],
[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1],
[-1,35,-1,-1,13,-1],
[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1],
[-1,15,-1,-1,-1,-1]]
Output: 4
Input: board = [[-1,-1],[-1,3]]
Output: 1这道题的思路是,我们需要先把棋盘转换成一个一维数组,然后用 BFS 来遍历整个图。
class Solution:
def snakesAndLadders(self, board: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if not board:
return 0
n = len(board)
cells = [None] * (n**2)
columns = list(range(0, n))
label = 0
for row in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
for column in columns:
cells[label] = (row, column)
label += 1
columns.reverse()
dist = [float("inf")] * (n * n)
dist[0] = 0
q = collections.deque([0])
def get_next(i):
row, col = cells[i]
return board[row][col] - 1 if board[row][col] != -1 else i
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
if cur == n * n - 1:
return dist[cur]
for i in range(cur + 1, min(cur + 7, n * n)):
nxt = get_next(i)
if dist[nxt] > dist[cur] + 1:
dist[nxt] = dist[cur] + 1
q.append(nxt)
return -1复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N^2),其中 N 是棋盘的边长。我们需要 O(N^2) 的时间来构建棋盘,同时每个格子最多只会被遍历一次,因此总时间复杂度为 O(N^2)。
- 空间复杂度:O(N^2),其中 N 是棋盘的边长。我们需要 O(N^2) 的空间来构建棋盘,同时需要 O(N^2) 的空间来保存 dist 数组。
433. minimum genetic mutation
这个题目的描述是,给出一个起始的基因序列,一个目标的基因序列,和一个基因库,我们需要判断从起始的基因序列到目标的基因序列,最少需要多少步。
test cases:
Input: startGene = "AACCGGTT", endGene = "AACCGGTA", bank = ["AACCGGTA"]
Output: 1
Input: startGene = "AACCGGTT", endGene = "AAACGGTA", bank = ["AACCGGTA", "AACCGCTA", "AAACGGTA"]
Output: 2这道题的思路是,我们需要用 BFS 来遍历整个图,然后用一个 visited 数组来记录已经访问过的基因序列。
class Solution:
def minMutation(self, startGene: str, endGene: str, bank: List[str]) -> int:
if not bank:
return -1
def can_mutate(gene):
res = []
for item in bank:
diff = 0
for i in range(len(item)):
if item[i] != gene[i]:
diff += 1
if diff == 1:
res.append(item)
return res
bank.append(startGene)
graph = collections.defaultdict(set)
for item in bank:
nxt_list = can_mutate(item)
for nxt in nxt_list:
graph[item].add(nxt)
q = collections.deque()
q.append((startGene, 0))
visited = set()
visited.add(startGene)
while q:
cur, step = q.popleft()
if cur == endGene:
return step
for nxt in graph[cur]:
if nxt not in visited:
q.append((nxt, step + 1))
visited.add(nxt)
return -1复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N^2 L),其中 N 是基因库的长度,L 是基因序列的长度。我们需要 O(N^2) 的时间来构建图,同时每个基因序列最多只会被遍历一次,因此总时间复杂度为 O(N^2 L)。
- 空间复杂度:O(N^2 * L),其中 N 是基因库的长度,L 是基因序列的长度。我们需要 O(N^2) 的空间来构建图,同时需要 O(N^2) 的空间来保存 visited 数组。
127. word ladder
这个题目的描述是,给出一个起始的单词,一个目标的单词,和一个单词字典,我们需要判断从起始的单词到目标的单词,最少需要多少步。
test cases:
Input: beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
Output: 5
Input: beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
Output: 0这道题的思路是,我们需要用 BFS 来遍历整个图,然后用一个 visited 数组来记录已经访问过的单词。
我们可以试着把每一个词的相邻词都输出出来,但是这样做,会导致 tle:
class Solution:
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
if endWord not in wordList or not endWord or not beginWord or not wordList:
return 0
wordList.append(beginWord)
wordList.append(endWord)
wordList = set(wordList)
graph = collections.defaultdict(set)
for word in wordList: # 这样存储的话,会导致tle,因为我们嵌套了两个for loop
for word2 in wordList:
if word != word2:
diff = 0
for i in range(len(beginWord)):
if word[i] != word2[i]:
diff += 1
if diff == 1:
graph[word].add(word2)
graph[word2].add(word)
visited = set()
visited.add(beginWord)
q = collections.deque([(beginWord, 1)])
while q:
current_word, level = q.popleft()
for i in range(len(beginWord)):
for word in graph[current_word]:
if word == endWord:
return level + 1
if word not in visited:
visited.add(word)
q.append((word, level + 1))
return 0不过我们可以优化一下,用*来代替每一个字母,这样就可以把每一个词的相邻词在一个 for 循环做到,就不会 tle 了:
class Solution:
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
if endWord not in wordList or not endWord or not beginWord or not wordList:
return 0
all_combo_dict = collections.defaultdict(list)
for word in wordList:
for i in range(len(beginWord)):
all_combo_dict[word[:i] + "*" + word[i + 1:]].append(word) # 这里存储的是每一个词的每一个index的相邻词
visited = set()
visited.add(beginWord)
q = collections.deque([(beginWord, 1)])
while q:
current_word, level = q.popleft()
for i in range(len(beginWord)):
temp = current_word[:i] + "*" + current_word[i+1:]
for word in all_combo_dict[temp]:
if word == endWord:
return level + 1
if word not in visited:
visited.add(word)
q.append((word, level + 1))
return 0复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(M^2 N),其中 M 是单词的长度,N 是单词的数量。我们需要 O(M^2) 的时间来构建所有的通用状态,同时每个单词需要花费 O(M) 的时间来构建通用状态。另外我们需要遍历所有的单词,所以总时间复杂度是 O(M^2 N)。
- 空间复杂度:O(M^2 N),其中 M 是单词的长度,N 是单词的数量。我们需要 O(M^2) 的空间来构建所有的通用状态,同时存储每个通用状态的所有单词。另外我们需要遍历所有的单词,所以总空间复杂度是 O(M^2 N)。
topological sort
207. course schedule
这个题目的描述是,给定一个课程的数量和一些课程的先修课程,我们需要判断是否能够完成所有的课程。
test cases:
Input: 2, [[1,0]]
Output: true
Input: 2, [[1,0],[0,1]]
Output: false这道题的思路是,先构建一个字典,用来记录每个节点的入度和出度,然后用 topological sort 来判断判断是不是能够完成所有的课程。
Topological sort:
class Solution:
def canFinish(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
indegree = {i: set() for i in range(numCourses)}
outdegree = defaultdict(set)
for u, v in prerequisites:
indegree[u].add(v)
outdegree[v].add(u)
print(indegree)
q = deque([i for i in indegree if not indegree[i]])
res = []
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
cur = q.popleft()
res.append(cur)
for nxt in outdegree[cur]:
indegree[nxt].remove(cur)
if not indegree[nxt]:
q.append(nxt)
print(res)
return True if len(res) == numCourses else False复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N + M),其中 N 是课程的数量,M 是先修课程的数量。在建图的过程中,我们需要 O(M) 的时间来找到每个节点的入度和出度。
- 空间复杂度:O(N + M),其中 N 是课程的数量,M 是先修课程的数量。我们需要 O(M) 的空间来存储图。
210. course schedule ii
这个题目的描述是,给定一个课程的数量和一些课程的先修课程,我们需要返回一个完成所有课程的顺序。
test cases:
Input: 2, [[1,0]]
Output: [0,1]
Input: 4, [[1,0],[2,0],[3,1],[3,2]]
Output: [0,1,2,3] or [0,2,1,3]这道题的思路是,先构建一个字典,用来记录每个节点的入度和出度,然后用 topological sort 来判断判断是不是能够完成所有的课程。
Topological sort:
class Solution:
def findOrder(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
indegree = {i: set() for i in range(numCourses)}
outdegree = defaultdict(set)
for u, v in prerequisites:
indegree[u].add(v)
outdegree[v].add(u)
q = deque([i for i in indegree if not indegree[i]])
res = []
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
cur = q.popleft()
res.append(cur)
for nxt in outdegree[cur]:
indegree[nxt].remove(cur)
if not indegree[nxt]:
q.append(nxt)
return res if len(res) == numCourses else []复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N + M),其中 N 是课程的数量,M 是先修课程的数量。在建图的过程中,我们需要 O(M) 的时间来找到每个节点的入度和出度。
- 空间复杂度:O(N + M),其中 N 是课程的数量,M 是先修课程的数量。我们需要 O(M) 的空间来存储图。
269. alien dictionary
这个题目的描述是,给定一个字典,里面的单词是按照字母顺序排列的,我们需要返回一个字母顺序。
test cases:
Input: [
"wrt",
"wrf",
"er",
"ett",
"rftt"
]
Output: "wertf"这道题的思路是,先通过比较相邻的两个单词,找到第一个不同的字母,然后将这个字母的顺序加入到字典中,然后用 topological sort 来判断判断是不是能够完成所有的课程。
Topological sort:
class Solution:
def alienOrder(self, words: List[str]) -> str:
outdegree = collections.defaultdict(set)
indegree = {c: set() for word in words for c in word}
for first, second in zip(words, words[1:]):
for c, d in zip(first, second):
if c != d:
if d not in outdegree[c]:
outdegree[c].add(d)
indegree[d].add(c)
break
else:
if len(second) < len(first):
return ""
res = []
q = collections.deque([c for c in indegree if not indegree[c]])
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
res.append(cur)
for nxt in outdegree[cur]:
indegree[nxt].remove(cur)
if not indegree[nxt]:
q.append(nxt)
if len(res) < len(indegree):
return ""
return "".join(res)复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N + M),其中 N 是课程的数量,M 是先修课程的数量。在建图的过程中,我们需要 O(M) 的时间来找到每个节点的入度和出度。
- 空间复杂度:O(N + M),其中 N 是课程的数量,M 是先修课程的数量。我们需要 O(M) 的空间来存储图。
二分图
785. is graph bipartite
这个题目的描述是,给定一个图,我们需要判断这个图是不是二分图。
test cases:
Input: [[1,3], [0,2], [1,3], [0,2]]
Output: true
Input: [[1,2,3], [0,2], [0,1,3], [0,2]]
Output: false这道题的思路是,我们可以用两种颜色来标记每个节点,然后用 BFS 来遍历每个节点,如果遍历到的节点的颜色和当前节点的颜色相同,那么就不是二分图。
BFS:
class Solution:
def isBipartite(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
n = len(graph)
color = [False] * n
visited = set()
def bfs(vertex):
q = collections.deque([vertex])
visited.add(vertex)
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
for nxt in graph[cur]:
if nxt not in visited:
color[nxt] = not color[cur]
visited.add(nxt)
q.append(nxt)
else:
if color[nxt] == color[cur]:
return False
return True
for vertex in range(n):
if bfs(vertex) == False:
return False
return TrueDFS:
class Solution:
def isBipartite(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
n = len(graph)
color = [False] * n
visited = [False] * n
def dfs(vertex):
visited[vertex] = True
for nxt in graph[vertex]:
if visited[nxt] == False:
visited[nxt] = True
color[nxt] = not color[vertex]
if dfs(nxt) == False:
return False
else:
if color[nxt] == color[vertex]:
return False
return True
for vertex in range(n):
if visited[vertex] == False:
if dfs(vertex) == False:
return False
return True复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N + M),其中 N 是图中的节点数,M 是图中的边数。在遍历图的过程中,我们需要对每个节点进行染色,并对每条边进行染色,时间复杂度均为 O(1)。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是图中的节点数。我们需要使用 O(N) 的空间记录每个节点的颜色,以及使用 O(N) 的空间记录每个节点的访问情况。
886. possible bipartition
这个题目的描述是,给定一个图,我们需要判断这个图能不能被分成两个部分,使得每个部分里面的节点都没有边相连。
test cases:
Input: N = 4, dislikes = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,4]]
Output: true
Input: N = 3, dislikes = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: false这道题的思路是,我们可以用两种颜色来标记每个节点,然后用 BFS 来遍历每个节点,如果遍历到的节点的颜色和当前节点的颜色相同,那么就不是二分图。
BFS:
class Solution:
def possibleBipartition(self, N: int, dislikes: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
for u, v in dislikes:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
color = [0] * (N + 1)
for i in range(1, N + 1):
if color[i] == 0:
q = collections.deque([i])
color[i] = 1
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
for nxt in graph[cur]:
if color[nxt] == 0:
color[nxt] = -color[cur]
q.append(nxt)
else:
if color[nxt] == color[cur]:
return False
return TrueDFS:
class Solution:
def possibleBipartition(self, N: int, dislikes: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
for u, v in dislikes:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
color = [0] * (N + 1)
for i in range(1, N + 1):
if color[i] == 0:
color[i] = 1
if self.dfs(i, color, graph) == False:
return False
return True
def dfs(self, vertex, color, graph):
for nxt in graph[vertex]:
if color[nxt] == 0:
color[nxt] = -color[vertex]
if self.dfs(nxt, color, graph) == False:
return False
else:
if color[nxt] == color[vertex]:
return False
return True复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N + M),其中 N 是图中的节点数,M 是图中的边数。在遍历图的过程中,我们需要对每个节点进行染色,并对每条边进行染色,时间复杂度均为 O(1)。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是图中的节点数。我们需要使用 O(N) 的空间记录每个节点的颜色,以及使用 O(N) 的空间记录每个节点的访问情况。








Comments NOTHING