前言
在这个专题,我们重点讨论链表相关的问题。
其实在很多的链表问题当中,我们都可以先建立一个 dummy node,这样做的好处是我们不需要对头节点进行特殊的处理,而且在最后返回的时候也比较方便。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
# 实现过程
# ...
return dummy.next基础题目
反转链表
206. Reverse Linked List
这道题的描述是反转一个链表,我们可以使用上面的方法来解决。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
Input: head = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]
Input: head = []
Output: []这道题的做法是,我们使用一个 dummy node,然后不断地把 cur.next 指向 dummy.next,然后把 dummy.next 指向 cur.next,这样就可以完成反转了。
我们可以简单用一个例子来说明这个过程:
dummy -> 1
dummy -> 2 -> 1
dummy -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
dummy -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
dummy -> 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head = ListNode(0)
cur = head
while cur:
nxt = cur.next
cur.next = dummy_head.next # 把当前节点的下一个节点指向dummy构建好的后面
dummy_head.next = cur # 把dummy的下一个节点指向当前节点
cur = nxt # 当前节点指向下一个节点
return dummy_head.next还有一种方法,不使用 dummy node,而是使用 prev 和 nxt 来直接维护。
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
prev = None
cur = head
while cur:
nxt = cur.next
cur.next = prev # 把当前节点的下一个节点指向prev
prev = cur # prev指向当前节点
cur = nxt
return prev还有一种 recursive 的做法:
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next: # 在只剩下两个的时候,直接停止
return head
p = self.reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next = head # 把当前的下下个指向自己
head.next = None # 把当前的下一个指向None
return p # 返回最后一个节点复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用一个 dummy node。
92. Reverse Linked List II
这道题的描述是反转链表的一部分,与上面题目不同的是,这道题的反转是从 left 到 right,我们可以使用上面的方法来解决。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
Output: [1,4,3,2,5]
Input: head = [5], left = 1, right = 1
Output: [5]这道题的做法是,我们使用一个 dummy node,不过这次我们需要先找到 left 和 right 的位置,然后再进行反转。
我们可以简单用一个例子来说明这个过程:
dummy -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
dummy -> 1 -> 3 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5
dummy -> 1 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 5有一个很好的图片解释:
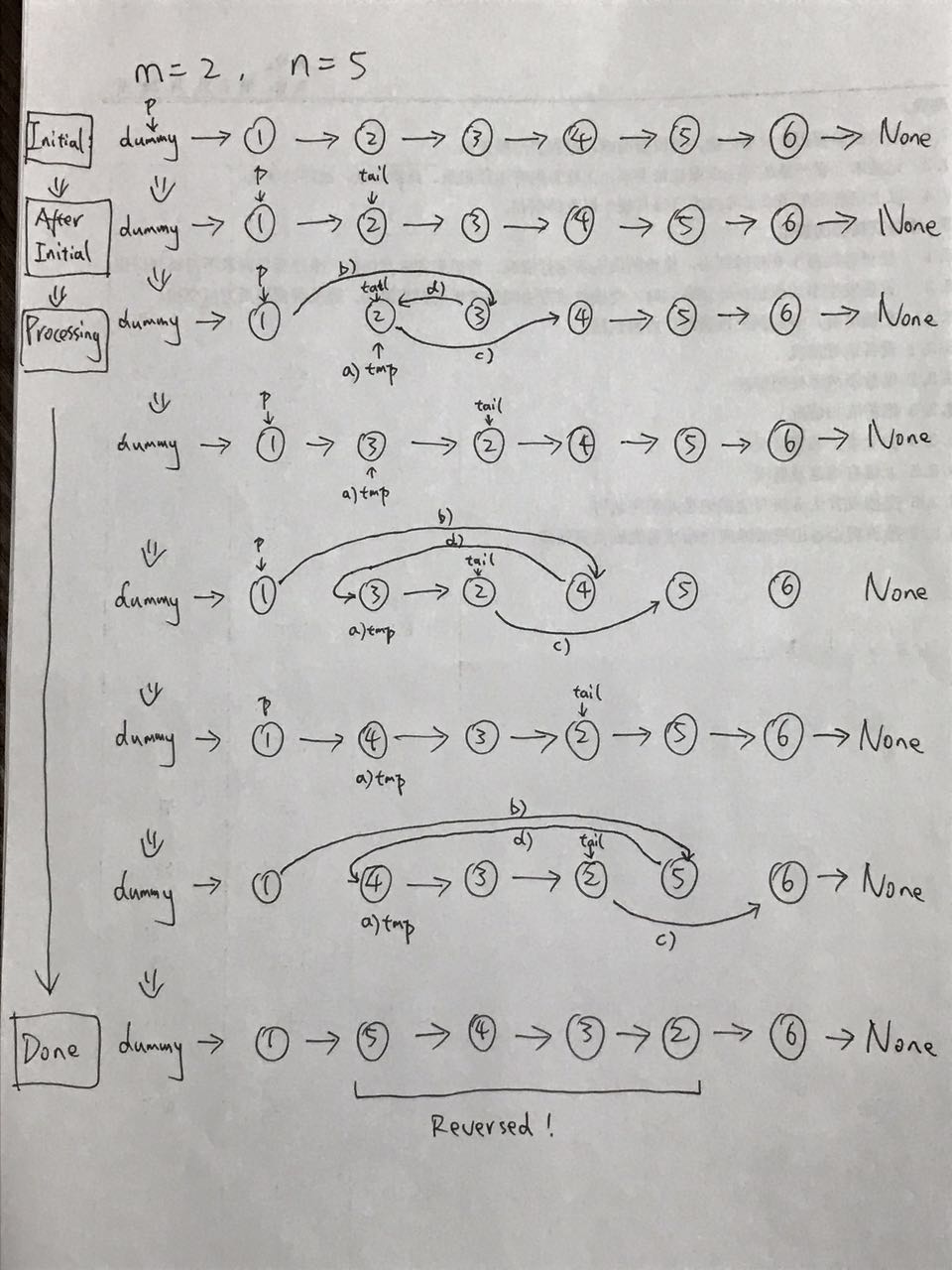
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, left: int, right: int) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
pre = dummy
for _ in range(left - 1):
pre = pre.next
cur = pre.next
for _ in range(right - left):
tmp = cur.next
cur.next = tmp.next
tmp.next = pre.next
pre.next = tmp
return dummy.next还有一种 recursive 的做法(实际上也是一种 backtracking 的做法,它的思路就是先找到 left 和 right 的位置,然后再进行反转):
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head, m, n):
if not head:
return None
left, right = head, head
stop = False
def recurseAndReverse(right, m, n):
nonlocal left, stop
if n == 1:
return
# Keep moving the right pointer one step forward until (n == 1)
right = right.next
if m > 1:
left = left.next
recurseAndReverse(right, m - 1, n - 1)
if left == right or right.next == left:
stop = True
# Until the boolean stop is false, swap data between the two pointers
if not stop:
left.val, right.val = right.val, left.val
left = left.next
recurseAndReverse(right, m, n)
return head复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用一个 dummy node。
25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
这道题的描述是反转链表的一部分,与上面题目不同的是,这道题的反转是每 k 个元素进行一次反转,我们可以使用上面的方法来解决。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
Output: [2,1,4,3,5]
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
Output: [3,2,1,4,5]这道题的做法是,我们使用一个 dummy node,不过这次我们要先找到每 k 个元素的位置,然后再进行反转。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution(object):
def reverseKGroup(self, head, k):
count, node = 0, head
while node and count < k:
node = node.next
count += 1
if count < k: return head
new_head, prev = self.reverse(head, count)
head.next = self.reverseKGroup(new_head, k)
return prev
def reverse(self, head, count):
prev, cur, nxt = None, head, head
while count > 0:
nxt = cur.next
cur.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = nxt
count -= 1
return (cur, prev)复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用一个 dummy node。
双指针
141. Linked List Cycle
这道题的描述是判断链表是否有环。
test cases:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: true这道题的做法是,我们使用两个指针,一个快指针,一个慢指针,如果快指针和慢指针相遇了,那么就说明有环。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
if not head:
return False
fast = slow = head
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if fast == slow:
return True
return False复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用两个指针。
876. Middle of the Linked List
这道题的描述是找到链表的中间节点。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [3,4,5]
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: [4,5,6]这道题的做法是,我们使用两个指针,一个快指针,一个慢指针,如果快指针到达了链表的尾部,那么慢指针就到达了链表的中间。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def middleNode(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return None
fast = slow = head
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
return slow复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用两个指针。
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
这道题的描述是找到两个链表的交点。
test cases:
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Intersected at '8'
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Intersected at '2'
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: No intersection这道题的做法是,我们使用两个指针,一个指针指向链表 A,一个指针指向链表 B,当指针到达了链表的尾部,那么就指向另一个链表的头部,这样当两个指针相遇的时候,就是两个链表的交点。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: Optional[ListNode], headB: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not headA or not headB:
return None
a, b = headA, headB
while a != b:
a = a.next if a else headB
b = b.next if b else headA
return a复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用两个指针。
203. Remove Linked List Elements
这道题的描述是删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Input: head = [], val = 1
Output: []
Input: head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
Output: []这道题的做法是,我们使用两个指针,一个指针指向当前节点,一个指针指向当前节点的前一个节点,当当前节点的值等于 val 的时候,我们就删除当前节点,然后将前一个节点的 next 指向当前节点的 next。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def removeElements(self, head: Optional[ListNode], val: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head = ListNode(-1)
dummy_head.next = head
prev, cur = dummy_head, head
while cur:
if cur.val == val:
prev.next = cur.next # 删除当前节点
else:
prev = prev.next # 前一个节点指向当前节点
cur = cur.next
return dummy_head.next复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用两个指针。
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
这道题的描述是删除链表中倒数第 n 个节点。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1
Output: [1]这道题的做法是,我们使用两个指针,一个快指针,一个慢指针,快指针先走 n 步,然后快慢指针一起走,当快指针到达了链表的尾部,那么慢指针就到达了链表的倒数第 n 个节点。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return None
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
fast = slow = dummy
for _ in range(n):
fast = fast.next
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy.next复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用两个指针。
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
这道题的描述是合并两个有序链表。
test cases:
Input: l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]
Input: l1 = [], l2 = []
Output: []
Input: l1 = [], l2 = [0]
Output: [0]这道题的做法是,我们使用一个 dummy node,然后遍历两个链表,把两个链表的值相加,然后把结果加入到 dummy node 的后面。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head = ListNode(-1)
prev = dummy_head
while list1 and list2:
if list1.val <= list2.val:
prev.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
prev = prev.next
else:
prev.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
prev = prev.next
if list1 and not list2:
prev.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
if list2 and not list1:
prev.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
return dummy_head.next复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用一个 dummy node。
2. Add Two Numbers
这道题的描述是给定两个链表,每个链表代表一个数字,我们需要把这两个数字相加,然后返回一个新的链表。
test cases:
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
Output: [7,0,8]
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
Output: [0]
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]这道题的做法是,我们使用一个 dummy node,然后遍历两个链表,把两个链表的值相加,然后把结果加入到 dummy node 的后面。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head = ListNode(0)
cur = dummy_head
carry = 0
while l1 or l2 or carry:
l1_val = l1.val if l1 else 0
l2_val = l2.val if l2 else 0
cur_sum = l1_val + l2_val + carry
carry = cur_sum // 10
new_node = ListNode(cur_sum % 10)
cur.next = new_node
cur = new_node
l1 = l1.next if l1 else None
l2 = l2.next if l2 else None
return dummy_head.next328. Odd Even Linked List
这道题的描述是给定一个链表,我们需要把链表的奇数节点放到偶数节点的前面。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [1,3,5,2,4]
Input: head = [2,1,3,5,6,4,7]
Output: [2,3,6,7,1,5,4]这道题的做法是,我们使用两个 dummy node,然后遍历链表,把奇数节点放到第一个 dummy node 的后面,把偶数节点放到第二个 dummy node 的后面,最后把第一个 dummy node 的尾部和第二个 dummy node 的头部连接起来。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def oddEvenList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return None
dummy = ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head
odd, even = head, head.next
connection_point = even
while even and even.next:
odd.next = odd.next.next
odd = odd.next
even.next = even.next.next
even = even.next
odd.next = connection_point
return dummy.next复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用两个 dummy node。
86. Partition List
这道题的描述是给定一个链表和一个值 x,我们需要把链表中小于 x 的节点放到大于等于 x 的节点的前面。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3
Output: [1,2,2,4,3,5]
Input: head = [2,1], x = 2
Output: [1,2]这道题的做法是,我们使用两个 dummy node,然后遍历链表,把小于 x 的节点放到第一个 dummy node 的后面,把大于等于 x 的节点放到第二个 dummy node 的后面,最后把第一个 dummy node 的尾部和第二个 dummy node 的头部连接起来。
那么实现的代码就是:
def partition(self, head: Optional[ListNode], x: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return None
head1 = cur1 = ListNode()
head2 = cur2 = ListNode()
while head:
if head.val < x:
cur1.next = head
cur1 = cur1.next
else:
cur2.next = head
cur2 = cur2.next
head = head.next
cur1.next = head2.next
cur2.next = None
return head1.next其他类型
82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
这道题的描述是删除链表中的重复元素。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5]
Output: [1,2,5]
Input: head = [1,1,1,2,3]
Output: [2,3]这道题的做法是,我们使用一个 dummy node,然后遍历链表,如果当前节点和下一个节点的值相同,那么我们就需要删除这两个节点,如果不相同,那么我们就把当前节点加入到 dummy node 的后面。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return None
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
pre = dummy
cur = head
while cur:
while cur.next and cur.val == cur.next.val:
cur = cur.next
if pre.next == cur:
pre = pre.next
else:
pre.next = cur.next
cur = cur.next
return dummy.next复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用两个指针。
24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
这道题的描述是交换链表中的相邻两个元素。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [2,1,4,3]
Input: head = []
Output: []
Input: head = [1]
Output: [1]这道题的做法是,我们使用一个 dummy node,不过这次我们要先找到每两个元素的位置,然后再进行反转。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
pre = dummy
while pre.next and pre.next.next:
first = pre.next
second = pre.next.next
# 把三个node(pre,first,second)重新用他们的next链接,注意顺序!
pre.next = second
first.next = second.next
second.next = first
# pre走到下一个
pre = first
return dummy.next
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用一个 dummy node。
高级组合题
61. Rotate List
这道题的描述是旋转链表,我们可以使用上面的方法来解决。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4
Output: [2,0,1]这道题的做法是,我们使用一个 dummy node,先主动奥找到链表的长度,形成一个环,然后找到新的头结点的前一个节点,再断开环。
那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def rotateRight(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
cur = head
length = 1 # 自己也算一个
# 拿到链表的长度
while cur.next:
cur = cur.next
length += 1
# 把链表连成环
cur.next = head
# 求余拿到真正的k
k = k % length
# 找到新的头结点的前一个节点
for i in range(length - k):
cur = cur.next
head = cur.next
cur.next = None # 断开环
return head复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用一个 dummy node。
143. Reorder List
这道题的描述是重排链表,我们可以使用上面的方法来解决。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,4,2,3]
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [1,5,2,4,3]这道题的做法是,我们使用一个 dummy node,然后分为三个步骤:
- 找到链表的中间位置
- 反转后半部分
- 重新连接
用一个例子解释就是:
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
1. 找到链表的中间位置
slow = 3
2. 反转后半部分
1 -> 2 5 -> 4 -> 3
3. 重新连接
1 -> 5 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3那么实现的代码就是:
class Solution:
def reorderList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead.
"""
if not head:
return None
# 找到链表的中间位置
slow, fast = head, head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# 反转后半部分
prev = None
cur = slow
while cur:
nxt = cur.next
cur.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = nxt
# 重新连接
first, second = head, prev
while second.next:
first.next, first = second, first.next
second.next, second = first, second.next复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用一个 dummy node。
234. Palindrome Linked List
这道题的描述是回文链表,我们可以使用上面的方法来解决。
test cases:
Input: head = [1,2,2,1]
Output: true
Input: head = [1,2]
Output: false这道题的做法是,我们使用一个 dummy node,然后分为三个步骤:
- 找到链表的中间位置
- 反转后半部分
- 判断是否相等
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
# 找到链表的中间位置
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
# 如果是奇数,那么slow再往前走一步,要不然会多一个
if fast:
slow = slow.next
# 反转后半部分
def reverse(head):
if not head:
return None
prev = None
cur = head
while cur:
nxt = cur.next
cur.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = nxt
return prev
# 判断是否相等
new_head = reverse(slow)
while new_head:
if head.val != new_head.val:
return False
head = head.next
new_head = new_head.next
return True复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),原因是我们需要遍历整个链表。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),原因是我们只需要使用一个 dummy node。








Comments NOTHING