前言
在双指针题目中,分有两种情况,第一种是异向双指针,第二种是同向双指针。
异向双指针一般是指一个指针从左向右,另一个指针从右向左,比如在二分查找中,我们就是用了异向双指针。
同向双指针一般是指两个指针都从左向右,或者都从右向左,比如在链表中,我们就是用了同向双指针。
接下来有一些题型去探讨了各种双指针的使用方法,让我们先看看!
基础题
↓ 点击题目就可以直接跳转到 leetcode 题目页面 ↓
125. Valid Palindrome
这道题的描述就是判断一个字符串是否是回文串.
test cases:
Input: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
Output: true
Explanation: "amanaplanacanalpanama" is a palindrome.我们可以用双指针来做,一个指针从左向右,一个指针从右向左,然后判断两个指针指向的字符是否相等,如果不相等,那么就不是回文串,如果相等,那么就继续向中间移动。
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, s: str) -> bool:
left, right = 0, len(s) - 1
while left < right:
while left < right and not s[left].isalnum():
left += 1
while left < right and not s[right].isalnum():
right -= 1
if s[left].lower() != s[right].lower():
return False
left += 1
right -= 1
return True复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),因为每个字符都会被遍历一次
- 空间复杂度:O(1),因为只用了常数个变量
680. Valid Palindrome II
这道题是上一道题的变种,这道题的描述是,给定一个字符串,我们可以删除一个字符,判断是否能构成回文串。
test cases:
Input: s = "aba"
Output: true
Input: s = "abca"
Output: true
Explanation: You could delete the character 'c'.
Input: s = "abc"
Output: false我们可以用双指针来做,一个指针从左向右,一个指针从右向左,然后判断两个指针指向的字符是否相等,如果不相等,那么就删除左指针指向的字符,或者删除右指针指向的字符,然后判断剩下的字符串是否是回文串,如果是,那么就返回 true,否则就返回 false。
class Solution:
def validPalindrome(self, s: str) -> bool:
start, end = 0, len(s) - 1
while start < end:
if s[start] != s[end]:
left = s[start: end] # 删除左指针指向的字符
right = s[start + 1: end + 1] # 删除右指针指向的字符
return left == left[::-1] or right == right[::-1]
start += 1
end -= 1
return True复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),因为每个字符都会被遍历一次
- 空间复杂度:O(1),因为只用了常数个变量
392. Is Subsequence
这道题的描述是,给定两个字符串 s 和 t,判断 s 是否是 t 的子序列。
test cases:
Input: s = "abc", t = "ahbgdc"
Output: true
Input: s = "axc", t = "ahbgdc"
Output: false我们可以用同向双指针来做,一个指针指向 s,一个指针指向 t,然后判断两个指针指向的字符是否相等,如果相等,那么就继续向后移动,如果不相等,那么就继续向后移动 t 指针,直到 t 指针指向的字符和 s 指针指向的字符相等,然后再继续向后移动。
class Solution:
def isSubsequence(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
i, j = 0, 0
while i < len(s) and j < len(t):
if s[i] == t[j]:
i += 1
j += 1
return i == len(s)复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),因为每个字符都会被遍历一次
- 空间复杂度:O(1),因为只用了常数个变量
167. Two Sum II - Input Array Is Sorted
这道题的描述是,给定一个升序数组和一个目标值,找到数组中两个数的和等于目标值,返回这两个数的下标。
test cases:
Input: numbers = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [1,2]
Explanation: The sum of 2 and 7 is 9. Therefore, index1 = 1, index2 = 2. We return [1, 2].
Input: numbers = [2,3,4], target = 6
Output: [1,3]
Explanation: The sum of 2 and 4 is 6. Therefore index1 = 1, index2 = 3. We return [1, 3].
Input: numbers = [-1,0], target = -1
Output: [1,2]
Explanation: The sum of -1 and 0 is -1. Therefore index1 = 1, index2 = 2. We return [1, 2].我们可以用异向双指针来做,一个指针指向数组的最左边,一个指针指向数组的最右边,然后判断两个指针指向的数的和是否等于目标值,如果等于,那么就返回两个指针的下标,如果小于目标值,那么就向右移动左指针,如果大于目标值,那么就向左移动右指针。
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, numbers: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
left, right = 0, len(numbers) - 1
while left < right:
if numbers[left] + numbers[right] == target:
return [left + 1, right + 1]
elif numbers[left] + numbers[right] < target:
left += 1
else:
right -= 1
return [-1, -1]复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),因为每个字符都会被遍历一次
- 空间复杂度:O(1),因为只用了常数个变量
11. Container With Most Water
这道题的描述是,给定一个数组,数组中的每个元素代表一个柱子的高度,然后找到两个柱子,使得这两个柱子和 x 轴围成的面积最大。
test cases:
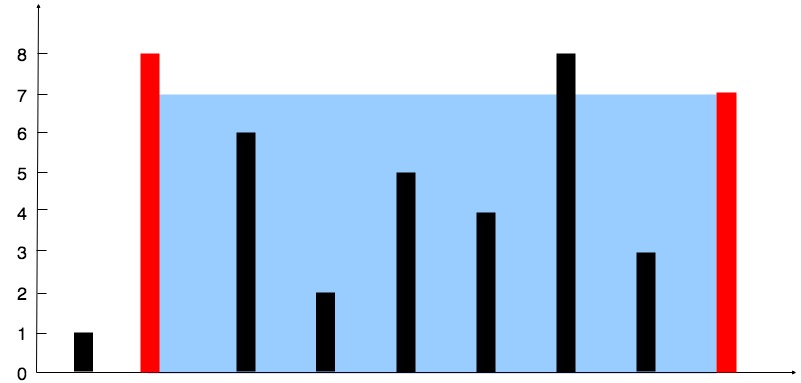
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.我们可以用异向双指针来做,一个指针指向数组的最左边,一个指针指向数组的最右边,然后计算两个指针指向的柱子围成的面积,然后判断两个指针指向的柱子的高度,如果左指针指向的柱子的高度小于右指针指向的柱子的高度,那么就向右移动左指针,如果左指针指向的柱子的高度大于右指针指向的柱子的高度,那么就向左移动右指针。
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
left, right = 0, len(height) - 1
res = 0
while left < right:
res = max(res, min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left))
if height[left] < height[right]:
left += 1
else:
right -= 1
return res复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),因为每个字符都会被遍历一次
- 空间复杂度:O(1),因为只用了常数个变量
15. 3Sum
这道题的描述是,给定一个数组,找到数组中所有三个数的和等于 0 的三元组,返回这些三元组。
test cases:
Input: nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
Output: [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
Input: nums = []
Output: []
Input: nums = [0]
Output: []我们可以用异向双指针来做,一个指针指向数组的最左边,一个指针指向数组的最右边,然后判断两个指针指向的数的和是否等于目标值,如果等于,那么就返回两个指针的下标,如果小于目标值,那么就向右移动左指针,如果大于目标值,那么就向左移动右指针。
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
nums.sort()
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] > 0:
break
if i == 0 or nums[i - 1] != nums[i]:
self.twoSum(nums, i, res)
return res
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], i: int, res: List[List[int]]):
seen = set()
j = i + 1
while j < len(nums):
complement = -nums[i] - nums[j]
if complement in seen:
res.append([nums[i], nums[j], complement])
while j + 1 < len(nums) and nums[j] == nums[j + 1]:
j += 1
seen.add(nums[j])
j += 1我们也可以使用隔板法来做,gap 当作隔板,左边的指针指向隔板左边,右边的指针指向隔板右边,然后判断左指针指向的数加上隔板指向的数加上右指针指向的数是否等于 0,如果等于 0,那么就返回三个指针的下标,如果小于 0,那么就向右移动左指针,如果大于 0,那么就向左移动右指针。
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
nums.sort()
if not nums or len(nums) < 3:
return []
res = set()
for gap in range(1, len(nums) - 1):
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left < gap and right > gap:
if nums[left] + nums[gap] + nums[right] < 0: # 说明左边的数太小了,需要增大
left += 1
elif nums[left] + nums[gap] + nums[right] > 0: # 说明右边的数太大了,需要减小
right -= 1
else:
res.add((nums[left], nums[gap], nums[right]))
left += 1
right -= 1
return res复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2),因为每个字符都会被遍历一次
- 空间复杂度:O(1),因为只用了常数个变量
inplace 替换题
283. Move Zeroes
这道题的描述是,给定一个数组,将数组中的 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非 0 元素的相对顺序。
test cases:
Input: [0,1,0,3,12]
Output: [1,3,12,0,0]这道题的思路是,使用两个指针 fast 和 slow, fast 指针用来遍历数组,slow 指针用来指向非 0 元素的位置,然后将 fast 指针指向的元素赋值给 slow 指针指向的元素,然后 fast 指针向前移动一步,slow 指针向前移动一步,直到 fast 指针指向的元素为 0,然后 fast 指针向前移动一步,slow 指针不动,直到 fast 指针指向的元素不为 0,然后将 fast 指针指向的元素赋值给 slow 指针指向的元素,然后 fast 指针向前移动一步,slow 指针向前移动一步,直到 fast 指针到达数组的末尾,然后将 slow 指针指向的元素到数组的末尾都赋值为 0。
class Solution:
def moveZeroes(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
slow, fast = 0, 0
while fast < len(nums):
while fast + 1 < len(nums) and nums[fast] == 0:
fast += 1
nums[slow] = nums[fast]
slow += 1
fast += 1
while slow < len(nums):
if nums[slow] != 0:
nums[slow] = 0
slow += 1复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),因为每个字符都会被遍历一次
- 空间复杂度:O(1),因为只用了常数个变量
27. Remove Element
这道题的描述是,给定一个数组和一个值,将数组中所有等于这个值的元素删除,并返回删除后数组的长度。
test cases:
Input: nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3
Output: 2, nums = [2,2]这道题的思路是,使用两个指针 fast 和 slow, fast 指针用来遍历数组,slow 指针用来指向非 val 元素的位置,然后将 fast 指针指向的元素赋值给 slow 指针指向的元素,然后 fast 指针向前移动一步,slow 指针向前移动一步,直到 fast 指针指向的元素为 val,然后 fast 指针向前移动一步,slow 指针不动,直到 fast 指针指向的元素不为 val,然后将 fast 指针指向的元素赋值给 slow 指针指向的元素,然后 fast 指针向前移动一步,slow 指针向前移动一步,直到 fast 指针到达数组的末尾,然后返回 slow 指针的值。
class Solution:
def removeElement(self, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int:
slow, fast = 0, 0
while fast < len(nums):
while fast + 1 < len(nums) and nums[fast] == val:
fast += 1
nums[slow] = nums[fast]
slow += 1
fast += 1
# 如果最后一个元素是 val,那么 slow 指针指向的元素就是 val,所以需要减 1
if len(nums) >= 1 and nums[-1] == val:
return slow - 1
return slow复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),因为每个字符都会被遍历一次
- 空间复杂度:O(1),因为只用了常数个变量
26. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
这道题的描述是,给定一个排序数组,删除重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次,并返回删除后数组的长度。
test cases:
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output: 2, nums = [1,2]这道题的思路是,使用两个指针 fast 和 slow, fast 指针用来遍历数组,slow 指针用来指向非重复元素的位置,然后将 fast 指针指向的元素赋值给 slow 指针指向的元素,然后 fast 指针向前移动一步,slow 指针向前移动一步,直到 fast 指针指向的元素和 slow 指针指向的元素不相等,然后将 fast 指针指向的元素赋值给 slow 指针指向的元素,然后 fast 指针向前移动一步,slow 指针向前移动一步,直到 fast 指针到达数组的末尾,然后返回 slow 指针的值。
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
slow, fast = 0, 0
while fast < len(nums):
while fast + 1 < len(nums) and nums[fast] == nums[fast + 1]:
fast += 1
nums[slow] = nums[fast]
slow += 1
fast += 1
return slow复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),因为每个字符都会被遍历一次
- 空间复杂度:O(1),因为只用了常数个变量
80. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
这道题的描述是,给定一个排序数组,删除重复的元素,使得每个元素最多只出现两次,并返回删除后数组的长度。
test cases:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3]
Output: 5, nums = [1,1,2,2,3]这道题和前面的区别是,前面的题目是每个元素只出现一次,而这道题是每个元素最多只出现两次,所以需要增加一个变量 count,用来记录当前元素出现的次数,当 count 大于等于 2 的时候,就不再将 fast 指针指向的元素赋值给 slow 指针指向的元素,而是只移动 fast 指针,直到 fast 指针指向的元素和 slow 指针指向的元素不相等,然后将 fast 指针指向的元素赋值给 slow 指针指向的元素,然后 fast 指针向前移动一步,slow 指针向前移动一步,直到 fast 指针到达数组的末尾,然后返回 slow 指针的值。
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
slow, fast = 0, 0
count = 0
while fast < len(nums):
while fast + 1 < len(nums) and nums[fast] == nums[fast + 1]:
fast += 1
count += 1
if count < 2:
nums[slow] = nums[fast]
slow += 1
nums[slow] = nums[fast]
slow += 1
fast += 1
count = 0
return slow







Comments NOTHING